Mouse model validation & phenotyping
Mouse model validation & phenotyping
What is mouse model validation?
Mouse model validation is a check to confirm that the knockout, knock-in, humanized or transgenic mouse model has the correctly engineered allele at the DNA level. Further validation can occur at the level of mRNA expression, protein expression or phenotype.
What is mouse model phenotyping?
Mouse model phenotyping is the assessment of measurable physiological effects caused by genetic changes under specific conditions. This may include immune viability studies, basic morphological and/or behavioural analysis, immune checkpoint target validation, early determination of utility, characterisation under challenge and other pre-clinical mouse research.
Enquire for other phenotyping services:
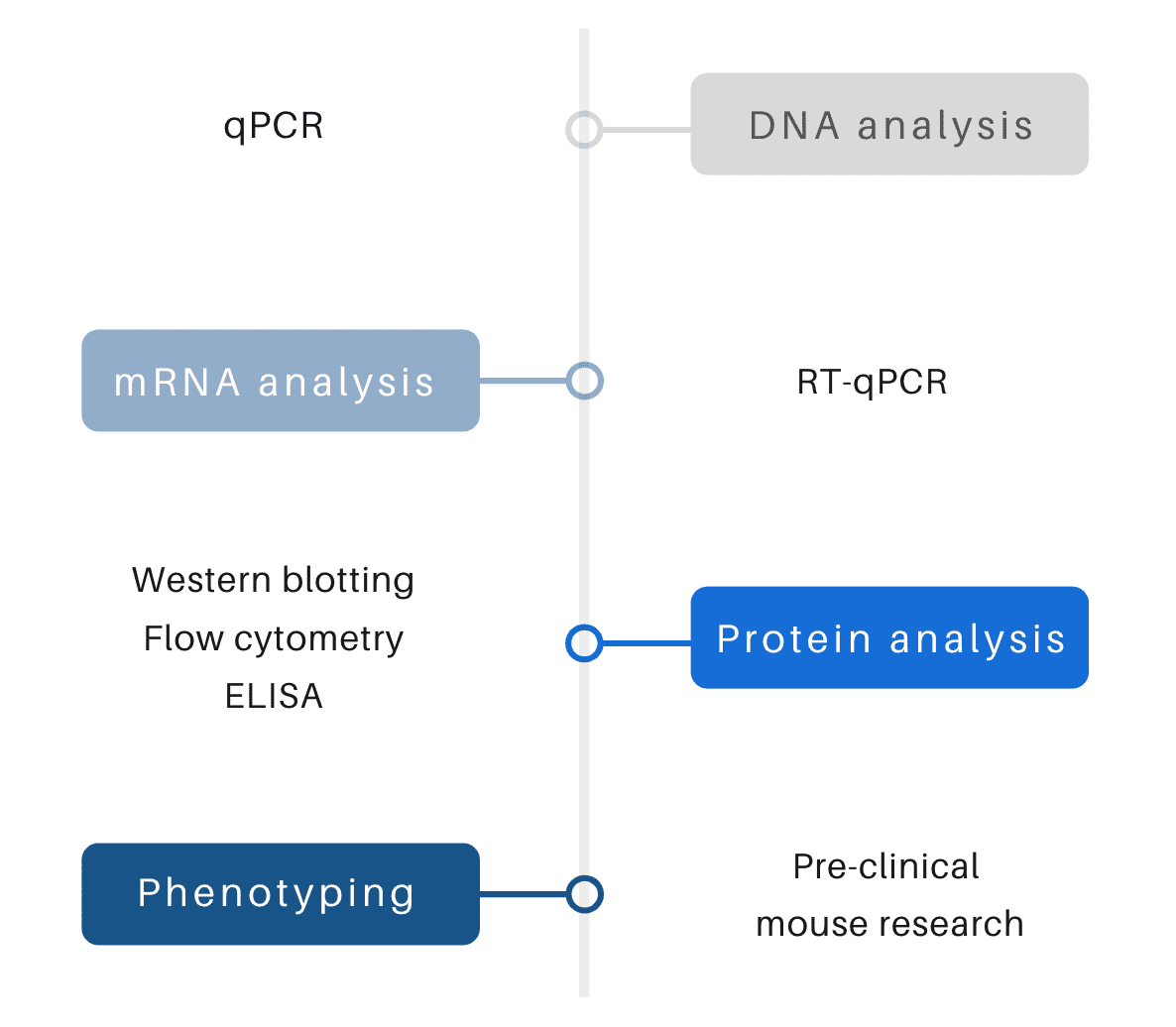
We use various technologies to validate and phenotype your mouse lines:
DNA Analysis
At the DNA level, validation of animal models is done by performing DNA analysis to ensure that the desired transgenic modification has been achieved and no unintended mutations have been introduced. Ozgene uses quantitative PCR (qPCR) at specific, unique sites of the targeting vector to ensure that the intended gene has been fully and correctly targeted. Genomic DNA screening is also used to detect any unintended insertional mutations.
mRNA analysis
At the mRNA level, expression of the modified gene is determined by quantifying mRNA as compared to the mRNA levels of the wild-type gene or that of other control genes. This is a valuable check to determine how the genetic modification has altered gene expression. Ozgene uses reverse transcription coupled with qPCR (RT-qPCR) to measure mRNA levels of cells or tissues from mouse models as an indication of relative gene expression.
Protein analysis
Protein expression is also a valuable piece of characterisation data. It relies on the availability of appropriate antibody reagents for analysis by western blotting, flow cytometry or ELISA. These assays provide data regarding changes to protein expression, protein size and the specificity of protein expression across various tissues and cell types. Since protein analysis is downstream of mRNA analysis, it can replace mRNA analysis for validation purposes.
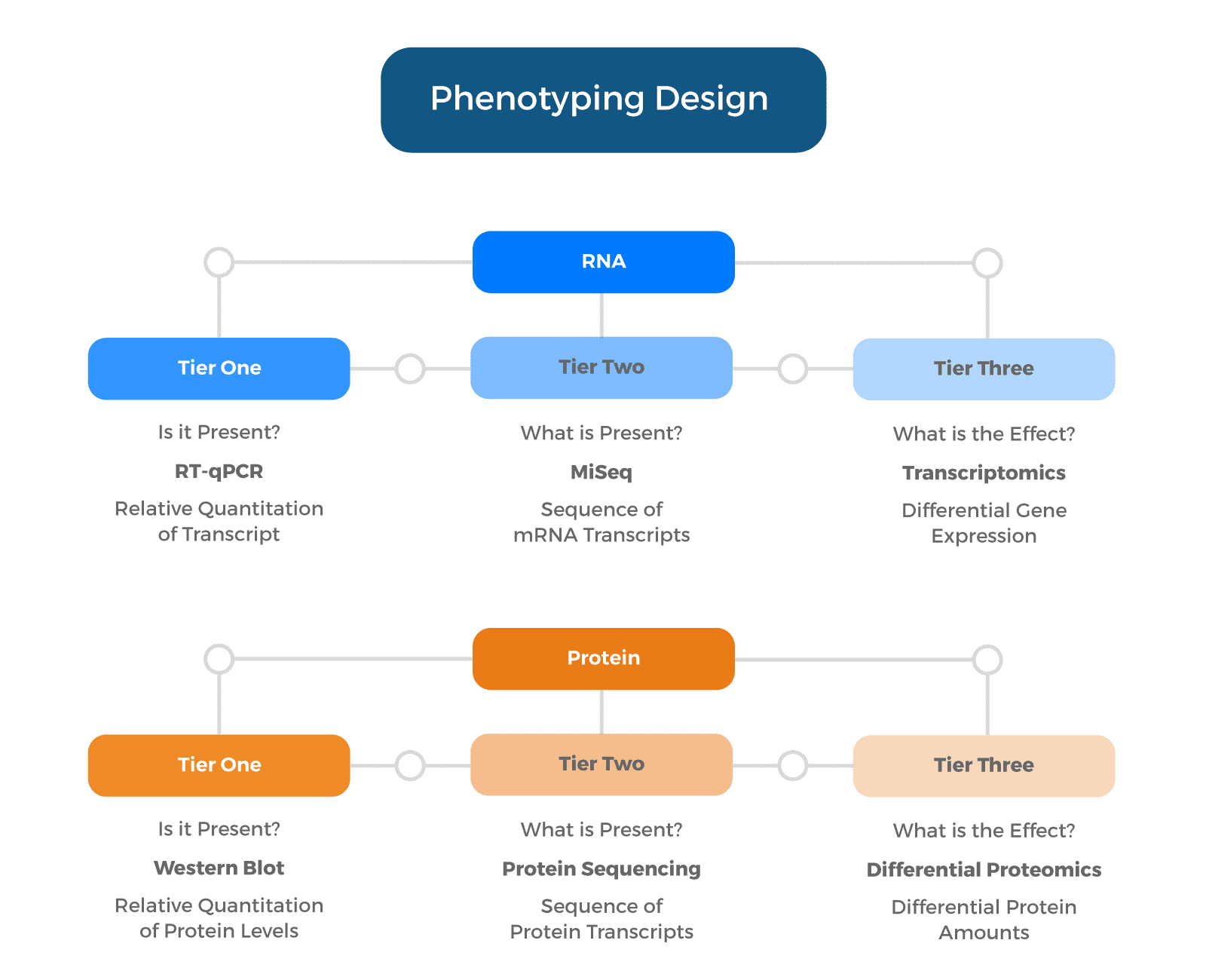
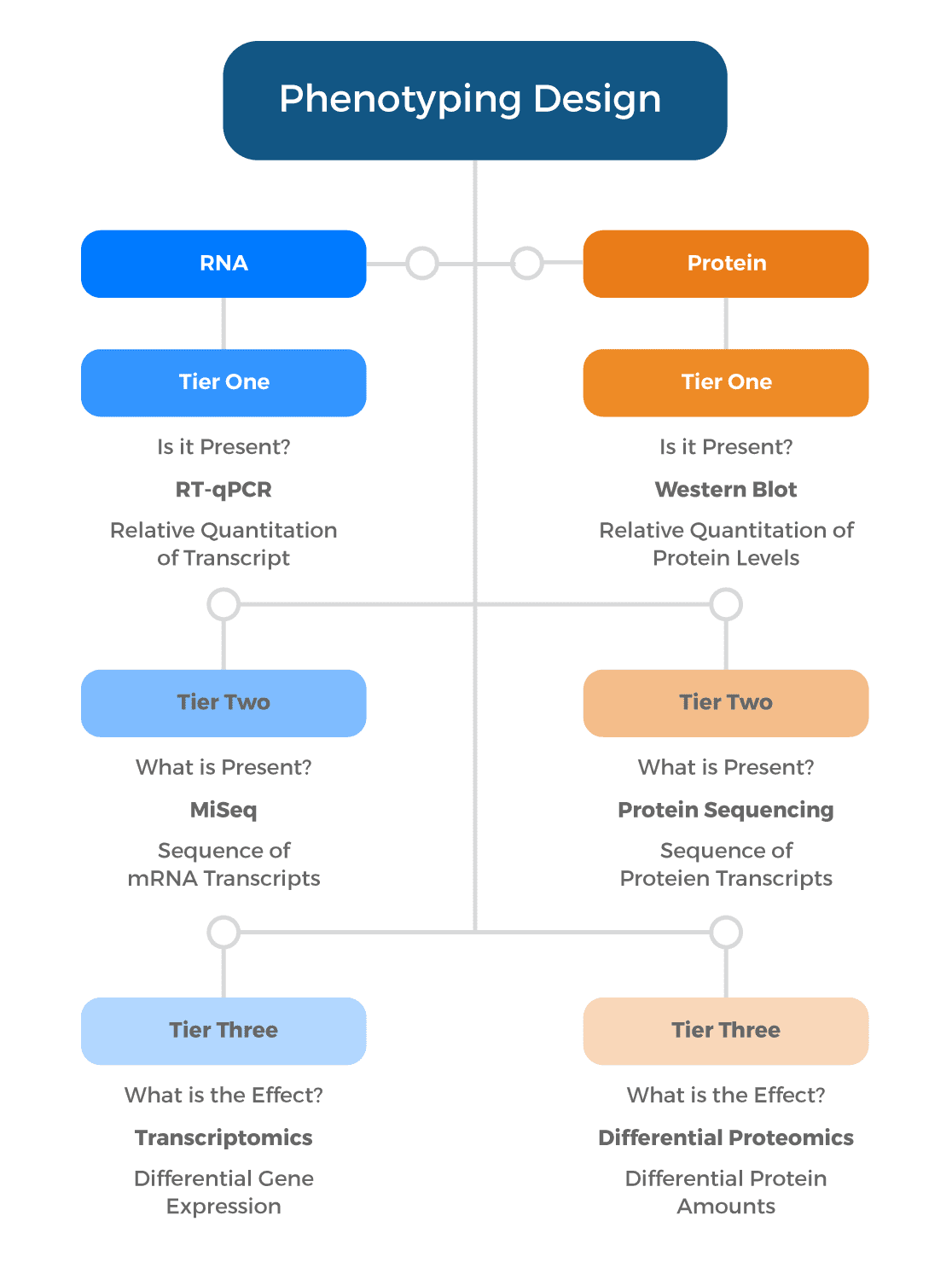
Validation of humanized alleles
Validating humanized alleles in transgenic mice is a critical step in biomedical research to understand the functional relevance of human genes and their impact on disease pathogenesis. Humanized alleles are genetically modified versions of mouse genes replaced with their human counterparts, allowing researchers to study human-specific mechanisms in a more physiologically relevant context.
The process involves precise genetic engineering, where human genomic DNA replaces the corresponding regions in mouse genes. Once transgenic mice carrying these humanized alleles are generated, rigorous validation is essential. This validation can be as simple as evaluating expression of the humanized alleles or as sophisticated as performing molecular, cellular, and physiological analyses to ensure the humanized alleles functions as planned to support the research aims.
Ozgene can perform gene expression and protein studies to validate the human gene’s expression patterns and functional properties. Furthermore, phenotypic characterization can be carried out and often includes behavioral tests, tissue histology, and functional assays which are compared to wild-type mice and disease models.
Validating humanized alleles in transgenic mice enables investigators to proceed with their research with confidence that their humanized model is functionally relevant for use in exploring human biology, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets, bridging the gap between experimental models and clinical applications.
Get in touch
We provide tailored preclinical solutions to support your research, from genetically modified mouse models to breeding and phenotyping. Request a free quote today.
Fill out the form, and our team will respond within two business days. For stock strain enquiries, contact Ozgene ARC at arc@ozgene.com. For additional contact options, visit our contact page.

